Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkyl Groups
Alkyl groups are derived from alkanes by removing one hydrogen atom, resulting in a substituent that can attach to a larger molecule. They are named based on the number of carbon atoms they contain, with common prefixes like 'methyl' (1 carbon), 'ethyl' (2 carbons), and 'propyl' (3 carbons). Understanding the structure and naming conventions of alkyl groups is essential for drawing and identifying them in organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Sodium Alkynide Alkylation
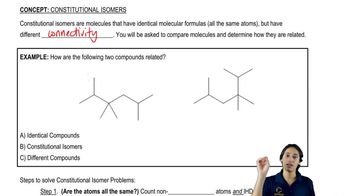
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms. This concept is crucial when discussing groups like (1-methylethyl) and (2-methylpropyl), as they can have different structures and properties despite having the same number of atoms. Recognizing these variations helps in accurately drawing and naming the groups.
Recommended video:
What is a constitutional isomer?
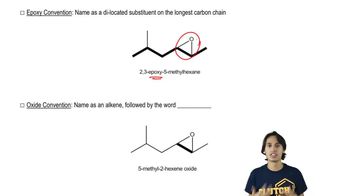
Common Naming Conventions
Common naming conventions in organic chemistry, such as IUPAC nomenclature, provide a systematic way to name chemical compounds based on their structure. For example, the 'isoamyl' group refers to a specific arrangement of carbon atoms in the (3-methylbutyl) group. Familiarity with these conventions is necessary for correctly identifying and naming the various alkyl groups presented in the question.
Recommended video:
How to name epoxides using the epoxy convention.
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 6:42m
6:42m