Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transduction
Transduction is a process by which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another via a bacteriophage, a type of virus that infects bacteria. During this process, the bacteriophage can accidentally incorporate bacterial DNA into its own genetic material and then transfer it to a new host cell during infection. This mechanism is significant for genetic diversity and horizontal gene transfer among bacteria.
Recommended video:
Bacteriophage
Bacteriophages, or phages, are viruses that specifically infect bacteria. They consist of genetic material encased in a protein coat and can replicate only within a bacterial host. Bacteriophages play a crucial role in transduction by serving as vectors for transferring genetic information between bacterial cells, influencing bacterial evolution and antibiotic resistance.
Recommended video:
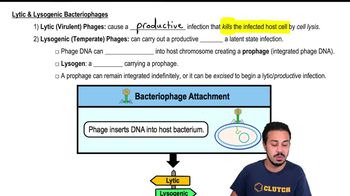
Lytic & Lysogenic Bacteriophages
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) refers to the movement of genetic material between organisms in a manner other than traditional reproduction. In bacteria, HGT can occur through mechanisms such as transduction, transformation, and conjugation, allowing for rapid adaptation and evolution. This process is essential for the spread of traits like antibiotic resistance among bacterial populations.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: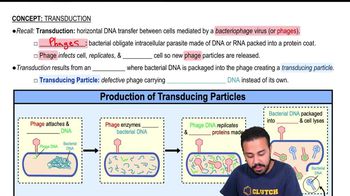


 6:49m
6:49m