Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Fungal Cytoplasmic Membranes
Fungal cytoplasmic membranes are essential structures that separate the interior of the fungal cell from its external environment. These membranes are primarily composed of a lipid bilayer, which includes unique components such as ergosterol, a sterol that is crucial for maintaining membrane integrity and fluidity. Understanding the composition and function of these membranes is vital for comprehending how antifungal agents exert their effects.
Recommended video:
Ergosterol
Ergosterol is a sterol found in the membranes of fungi, analogous to cholesterol in animal cells. It plays a critical role in stabilizing the membrane structure and is involved in various cellular processes. Many antifungal agents, such as azoles and polyenes, specifically target ergosterol, disrupting membrane integrity and leading to cell death, making it a key focus in antifungal therapy.
Antifungal Agents
Antifungal agents are medications used to treat fungal infections by targeting specific components of fungal cells. These agents can be classified into several categories, including azoles, polyenes, and echinocandins, each with distinct mechanisms of action. Understanding how these agents interact with fungal cell structures, particularly the cytoplasmic membrane and ergosterol, is essential for developing effective treatments and combating resistance.
Recommended video:
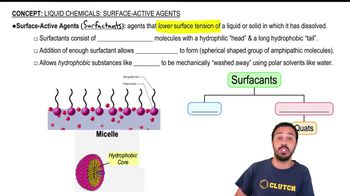
Liquid Chemicals: Surface-Active Agents
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: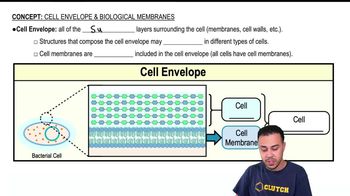

 5:09m
5:09m