Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Microbiology3h 21m
- Introduction to Microbiology16m
- Introduction to Taxonomy26m
- Scientific Naming of Organisms9m
- Members of the Bacterial World10m
- Introduction to Bacteria9m
- Introduction to Archaea10m
- Introduction to Eukarya20m
- Acellular Infectious Agents: Viruses, Viroids & Prions19m
- Importance of Microorganisms20m
- Scientific Method27m
- Experimental Design30m
- 2. Disproving Spontaneous Generation1h 18m
- 3. Chemical Principles of Microbiology3h 38m
- 4. Water1h 28m
- 5. Molecules of Microbiology2h 23m
- 6. Cell Membrane & Transport3h 28m
- Cell Envelope & Biological Membranes12m
- Bacterial & Eukaryotic Cell Membranes8m
- Archaeal Cell Membranes18m
- Types of Membrane Proteins8m
- Concentration Gradients and Diffusion9m
- Introduction to Membrane Transport14m
- Passive vs. Active Transport13m
- Osmosis33m
- Simple and Facilitated Diffusion17m
- Active Transport30m
- ABC Transporters11m
- Group Translocation7m
- Types of Small Molecule Transport Review9m
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis15m
- 7. Prokaryotic Cell Structures & Functions5h 52m
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells26m
- Binary Fission11m
- Generation Times16m
- Bacterial Cell Morphology & Arrangements35m
- Overview of Prokaryotic Cell Structure10m
- Introduction to Bacterial Cell Walls26m
- Gram-Positive Cell Walls11m
- Gram-Negative Cell Walls20m
- Gram-Positive vs. Gram-Negative Cell Walls11m
- The Glycocalyx: Capsules & Slime Layers12m
- Introduction to Biofilms6m
- Pili18m
- Fimbriae & Hami7m
- Introduction to Prokaryotic Flagella12m
- Prokaryotic Flagellar Structure18m
- Prokaryotic Flagellar Movement11m
- Proton Motive Force Drives Flagellar Motility5m
- Chemotaxis14m
- Review of Prokaryotic Surface Structures8m
- Prokaryotic Ribosomes16m
- Introduction to Bacterial Plasmids13m
- Cell Inclusions9m
- Endospores16m
- Sporulation5m
- Germination5m
- 8. Eukaryotic Cell Structures & Functions2h 18m
- 9. Microscopes2h 46m
- Introduction to Microscopes8m
- Magnification, Resolution, & Contrast10m
- Introduction to Light Microscopy5m
- Light Microscopy: Bright-Field Microscopes23m
- Light Microscopes that Increase Contrast16m
- Light Microscopes that Detect Fluorescence16m
- Electron Microscopes14m
- Reviewing the Different Types of Microscopes10m
- Introduction to Staining5m
- Simple Staining14m
- Differential Staining6m
- Other Types of Staining11m
- Reviewing the Types of Staining8m
- Gram Stain13m
- 10. Dynamics of Microbial Growth4h 36m
- Biofilms16m
- Growing a Pure Culture5m
- Microbial Growth Curves in a Closed System21m
- Temperature Requirements for Microbial Growth18m
- Oxygen Requirements for Microbial Growth22m
- pH Requirements for Microbial Growth8m
- Osmolarity Factors for Microbial Growth14m
- Reviewing the Environmental Factors of Microbial Growth12m
- Nutritional Factors of Microbial Growth30m
- Growth Factors4m
- Introduction to Cultivating Microbial Growth5m
- Types of Solid Culture Media4m
- Plating Methods16m
- Measuring Growth by Direct Cell Counts9m
- Measuring Growth by Plate Counts14m
- Measuring Growth by Membrane Filtration6m
- Measuring Growth by Biomass15m
- Introduction to the Types of Culture Media5m
- Chemically Defined Media3m
- Complex Media4m
- Selective Media5m
- Differential Media9m
- Reducing Media4m
- Enrichment Media7m
- Reviewing the Types of Culture Media8m
- 11. Controlling Microbial Growth4h 10m
- Introduction to Controlling Microbial Growth29m
- Selecting a Method to Control Microbial Growth44m
- Physical Methods to Control Microbial Growth49m
- Review of Physical Methods to Control Microbial Growth7m
- Chemical Methods to Control Microbial Growth16m
- Chemicals Used to Control Microbial Growth6m
- Liquid Chemicals: Alcohols, Aldehydes, & Biguanides15m
- Liquid Chemicals: Halogens12m
- Liquid Chemicals: Surface-Active Agents17m
- Other Types of Liquid Chemicals14m
- Chemical Gases: Ethylene Oxide, Ozone, & Formaldehyde13m
- Review of Chemicals Used to Control Microbial Growth11m
- Chemical Preservation of Perishable Products10m
- 12. Microbial Metabolism5h 16m
- Introduction to Energy15m
- Laws of Thermodynamics15m
- Chemical Reactions9m
- ATP20m
- Enzymes14m
- Enzyme Activation Energy9m
- Enzyme Binding Factors9m
- Enzyme Inhibition10m
- Introduction to Metabolism8m
- Negative & Positive Feedback7m
- Redox Reactions22m
- Introduction to Aerobic Cellular Respiration25m
- Types of Phosphorylation12m
- Glycolysis19m
- Entner-Doudoroff Pathway11m
- Pentose-Phosphate Pathway10m
- Pyruvate Oxidation8m
- Krebs Cycle16m
- Electron Transport Chain19m
- Chemiosmosis7m
- Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration19m
- Fermentation & Anaerobic Respiration23m
- 13. Photosynthesis2h 31m
- 14. DNA Replication2h 25m
- 15. Central Dogma & Gene Regulation7h 14m
- Central Dogma7m
- Introduction to Transcription20m
- Steps of Transcription22m
- Transcription Termination in Prokaryotes7m
- Eukaryotic RNA Processing and Splicing20m
- Introduction to Types of RNA9m
- Genetic Code25m
- Introduction to Translation30m
- Steps of Translation23m
- Review of Transcription vs. Translation12m
- Prokaryotic Gene Expression21m
- Review of Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Gene Expression13m
- Introduction to Regulation of Gene Expression13m
- Prokaryotic Gene Regulation via Operons27m
- The Lac Operon21m
- Glucose's Impact on Lac Operon25m
- The Trp Operon20m
- Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon11m
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation9m
- Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications16m
- Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control22m
- Eukaryotic Post-Transcriptional Regulation28m
- Post-Translational Modification6m
- Eukaryotic Post-Translational Regulation13m
- 16. Microbial Genetics4h 44m
- Introduction to Microbial Genetics11m
- Introduction to Mutations20m
- Methods of Inducing Mutations15m
- Prototrophs vs. Auxotrophs13m
- Mutant Detection25m
- The Ames Test14m
- Introduction to DNA Repair5m
- DNA Repair Mechanisms37m
- Horizontal Gene Transfer18m
- Bacterial Transformation11m
- Transduction32m
- Introduction to Conjugation6m
- Conjugation: F Plasmids18m
- Conjugation: Hfr & F' Cells19m
- Genome Variability21m
- CRISPR CAS11m
- 17. Biotechnology3h 0m
- 18. Viruses, Viroids, & Prions4h 56m
- Introduction to Viruses20m
- Introduction to Bacteriophage Infections14m
- Bacteriophage: Lytic Phage Infections12m
- Bacteriophage: Lysogenic Phage Infections17m
- Bacteriophage: Filamentous Phage Infections8m
- Plaque Assays9m
- Introduction to Animal Virus Infections10m
- Animal Viruses: 1. Attachment to the Host Cell7m
- Animal Viruses: 2. Entry & Uncoating in the Host Cell19m
- Animal Viruses: 3. Synthesis & Replication22m
- Animal Viruses: DNA Virus Synthesis & Replication14m
- Animal Viruses: RNA Virus Synthesis & Replication22m
- Animal Viruses: Antigenic Drift vs. Antigenic Shift9m
- Animal Viruses: Reverse-Transcribing Virus Synthesis & Replication9m
- Animal Viruses: 4. Assembly Inside Host Cell8m
- Animal Viruses: 5. Release from Host Cell15m
- Acute vs. Persistent Viral Infections25m
- COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2)14m
- Plant Viruses12m
- Viroids6m
- Prions13m
- 19. Innate Immunity7h 15m
- Introduction to Immunity8m
- Introduction to Innate Immunity17m
- Introduction to First-Line Defenses5m
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Skin13m
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Mucous Membrane9m
- First-Line Defenses: Chemical Barriers24m
- First-Line Defenses: Normal Microflora5m
- Introduction to Cells of the Immune System15m
- Cells of the Immune System: Granulocytes29m
- Cells of the Immune System: Agranulocytes25m
- Introduction to Cell Communication5m
- Cell Communication: Surface Receptors & Adhesion Molecules16m
- Cell Communication: Cytokines27m
- Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)45m
- Introduction to the Complement System24m
- Activation Pathways of the Complement System23m
- Effects of the Complement System23m
- Review of the Complement System12m
- Phagoctytosis21m
- Introduction to Inflammation18m
- Steps of the Inflammatory Response26m
- Fever8m
- Interferon Response25m
- 20. Adaptive Immunity7h 14m
- Introduction to Adaptive Immunity32m
- Antigens12m
- Introduction to T Lymphocytes38m
- Major Histocompatibility Complex Molecules20m
- Activation of T Lymphocytes21m
- Functions of T Lymphocytes25m
- Review of Cytotoxic vs Helper T Cells13m
- Introduction to B Lymphocytes27m
- Antibodies14m
- Classes of Antibodies35m
- Outcomes of Antibody Binding to Antigen15m
- T Dependent & T Independent Antigens21m
- Clonal Selection20m
- Antibody Class Switching17m
- Affinity Maturation14m
- Primary and Secondary Response of Adaptive Immunity21m
- Immune Tolerance28m
- Regulatory T Cells10m
- Natural Killer Cells16m
- Review of Adaptive Immunity25m
- 21. Principles of Disease6h 57m
- Symbiotic Relationships12m
- The Human Microbiome46m
- Characteristics of Infectious Disease47m
- Stages of Infectious Disease Progression26m
- Koch's Postulates26m
- Molecular Koch's Postulates11m
- Bacterial Pathogenesis36m
- Introduction to Pathogenic Toxins6m
- Exotoxins Cause Damage to the Host40m
- Endotoxin Causes Damage to the Host13m
- Exotoxins vs. Endotoxin Review13m
- Immune Response Damage to the Host15m
- Introduction to Avoiding Host Defense Mechanisms8m
- 1) Hide Within Host Cells5m
- 2) Avoiding Phagocytosis31m
- 3) Surviving Inside Phagocytic Cells10m
- 4) Avoiding Complement System9m
- 5) Avoiding Antibodies25m
- Viruses Evade the Immune Response27m
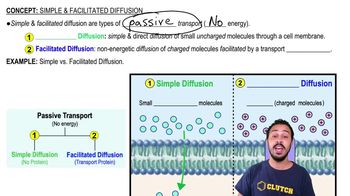
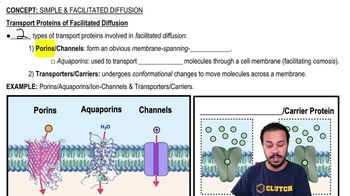
6. Cell Membrane & Transport
Simple and Facilitated Diffusion
Problem 3.1a
Textbook Question
Describe (or draw) an example of diffusion down a concentration gradient.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
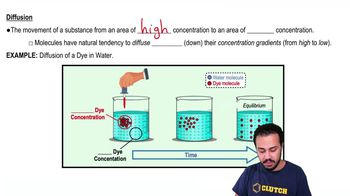
Identify a scenario where molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. For example, consider a drop of food coloring in a glass of water.
Understand that diffusion is a passive process, meaning it does not require energy input. Molecules move due to their kinetic energy.
Visualize or draw the initial state: a concentrated drop of food coloring in one part of the water, with clear water surrounding it.
Over time, observe or illustrate how the food coloring molecules spread out, moving from the area of high concentration (the drop) to areas of lower concentration (the surrounding water).
Recognize that eventually, the molecules will be evenly distributed throughout the water, reaching equilibrium where there is no net movement of molecules in any particular direction.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Diffusion
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This movement occurs due to the random motion of particles and continues until equilibrium is reached, where the concentration is uniform throughout the space. It is a fundamental concept in microbiology, as it explains how nutrients and gases are exchanged in biological systems.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Diffusion
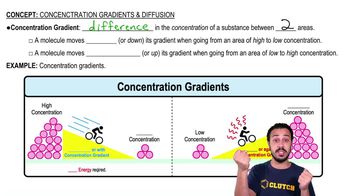
Concentration Gradient
A concentration gradient refers to the difference in the concentration of a substance between two areas. In biological contexts, this gradient drives the movement of substances across cell membranes, influencing processes such as nutrient uptake and waste removal. The steeper the gradient, the faster the rate of diffusion, making it a critical factor in cellular function.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Concentration Gradients and Diffusion
Equilibrium
Equilibrium in the context of diffusion occurs when the concentration of a substance is equal throughout a given space, resulting in no net movement of particles. This state is essential for maintaining homeostasis in biological systems, as it ensures that cells can efficiently manage the intake of necessary substances and the expulsion of waste products.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Diffusion

 5:10m
5:10mWatch next
Master Simple and Facilitated Diffusion with a bite sized video explanation from Jason Amores Sumpter
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice