Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Opsonization
Opsonization is a process that enhances the ability of phagocytes to recognize and engulf pathogens. It involves the binding of opsonins, such as antibodies or complement proteins, to the surface of microbes, marking them for destruction. This process increases the efficiency of phagocytosis, allowing immune cells to more effectively eliminate invaders.
Recommended video:
Phagocytosis
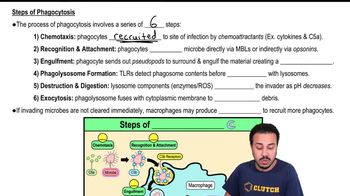
Phagocytosis is a cellular process where certain immune cells, known as phagocytes, engulf and digest pathogens or debris. During this process, the phagocyte extends its membrane to surround the target, forming a vesicle called a phagosome. This vesicle then fuses with lysosomes to degrade the engulfed material, playing a crucial role in the immune response.
Recommended video:
Pseudopods
Pseudopods are temporary, foot-like extensions of a cell's cytoplasm that are used by some cells, including phagocytes, to move and engulf particles. These structures are formed by the rearrangement of the cytoskeleton and allow the cell to change shape, facilitating the process of phagocytosis by surrounding and enclosing pathogens.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 2:19m
2:19m