Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lysogeny
Lysogeny is a viral replication cycle where a virus integrates its genetic material into the host cell's genome, allowing it to be replicated along with the host's DNA without causing immediate cell death. This process can lead to latent infections, where the virus remains dormant within the host until triggered to reactivate.
Recommended video:
Latent Viral Infections
Latent viral infections occur when a virus remains in a dormant state within the host's cells after initial infection. The virus can reactivate later, leading to symptoms or disease, which is characteristic of lysogenic cycles. Examples include herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus.
Recommended video:
Persistent Viral Infections
Slow Viral Infections
Slow viral infections are characterized by a gradual increase in viral load and symptoms over an extended period, often years. Unlike acute infections, these do not lead to immediate cell death but can result in chronic disease states, exemplifying the long-term effects of lysogenic cycles in certain viruses.
Recommended video:
Persistent Viral Infections
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution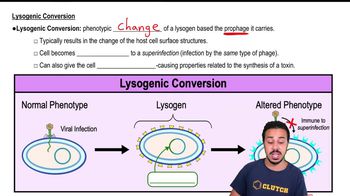



 5:27m
5:27m
