Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells are generally simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells. They lack membrane-bound organelles and a true nucleus, with their genetic material organized in a single circular chromosome. In contrast, eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus and complex structures, often forming multicellular organisms.
Recommended video:
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells
Characteristics of Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes, which include the Domains Bacteria and Archaea, typically possess a cell wall and reproduce asexually through binary fission, not mitosis. They can form endospores for survival in harsh conditions, but they do not have multicellular forms, which is a characteristic of many eukaryotes.
Recommended video:
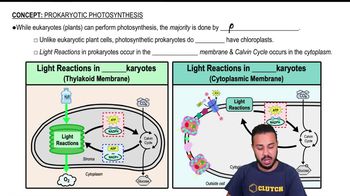
Prokaryotic Photosynthesis
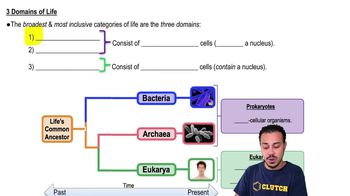
Domains of Life
Life is classified into three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Prokaryotes are found in the Bacteria and Archaea domains, while Eukarya includes all eukaryotic organisms. Understanding these domains is crucial for distinguishing the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic life forms.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 5:54m
5:54m