Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is a passive transport process that allows substances to cross membranes with the assistance of special proteins. This mechanism is crucial for the movement of large or charged molecules that cannot easily pass through the lipid bilayer. The process occurs down the concentration gradient, meaning substances move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration without the use of energy.
Recommended video:
Simple and Facilitated Diffusion
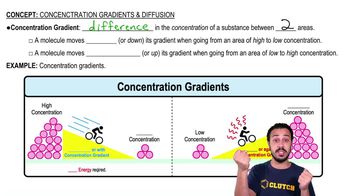
Chemical and Electrical Gradients
Chemical and electrical gradients refer to the differences in concentration and charge across a membrane. The chemical gradient is the difference in the concentration of a substance, while the electrical gradient is the difference in charge. Together, these gradients drive the movement of ions and molecules across the membrane, influencing processes like facilitated diffusion and active transport.
Recommended video:
Concentration Gradients and Diffusion
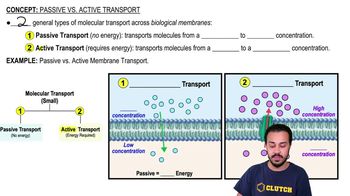
Passive vs. Active Transport
Transport mechanisms in cells can be classified as passive or active. Passive transport, such as facilitated diffusion, does not require energy and relies on the natural movement of molecules down their gradients. In contrast, active transport requires energy, usually in the form of ATP, to move substances against their gradients, allowing cells to maintain concentration differences essential for various cellular functions.
Recommended video:
Passive vs. Active Transport
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution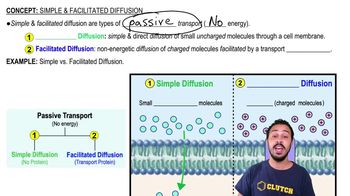

 4:18m
4:18m
