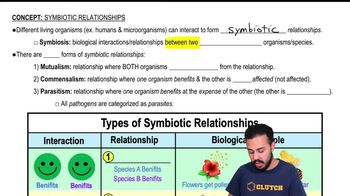
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Intermediate Hosts
Intermediate hosts are organisms that harbor the larval or juvenile stages of a parasite, which undergoes development before reaching its definitive host. In the case of Taenia saginata, which is a tapeworm, the definitive host is typically humans, while cattle serve as the intermediate hosts. Understanding the role of intermediate hosts is crucial for comprehending the life cycle of parasites.
Recommended video:
Taenia saginata
Taenia saginata, commonly known as the beef tapeworm, is a parasitic flatworm that primarily infects humans through the consumption of undercooked beef containing its larvae. It is important to recognize that humans are not intermediate hosts for this parasite; instead, they are the definitive hosts where the adult tapeworm resides in the intestines. This distinction is vital for understanding transmission and infection prevention.
Host-Parasite Relationships
Host-parasite relationships describe the interactions between a host organism and a parasitic organism. These relationships can be complex, involving various adaptations by the parasite to exploit the host for survival and reproduction. In the context of Taenia saginata, recognizing that humans serve as the definitive host helps clarify the dynamics of infection and the importance of proper food handling to prevent transmission.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: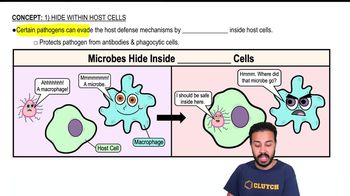

 5:09m
5:09m