Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exocytosis
Exocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are exported from a cell through vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane. This mechanism is crucial for the secretion of proteins and other molecules synthesized in the cell, particularly those produced in the endoplasmic reticulum and processed in the Golgi apparatus. The vesicles bud off from the Golgi, carrying their contents to the cell surface, where they release their cargo into the extracellular space.
Recommended video:
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is the process by which cells internalize substances from their external environment. This occurs through the invagination of the plasma membrane, which engulfs the material and forms a vesicle that brings it into the cell. There are different types of endocytosis, including phagocytosis for solid particles and pinocytosis for liquids, allowing cells to uptake nutrients, signaling molecules, and other essential substances.
Recommended video:
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Vesicular Transport
Vesicular transport refers to the movement of materials within vesicles in and out of cells. This process is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating communication between organelles. Vesicles can transport proteins, lipids, and other molecules, playing a key role in both exocytosis and endocytosis, and ensuring that cells can efficiently manage their internal and external environments.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: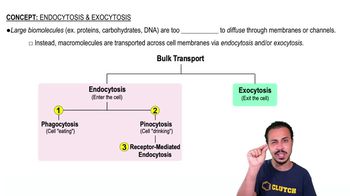


 2:02m
2:02m