Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Infection Control
Infection control refers to the practices and procedures used to prevent the spread of infections in healthcare settings. This field emerged from the understanding of how pathogens are transmitted and the importance of hygiene, sterilization, and isolation techniques. Key figures in this area, such as Florence Nightingale and Joseph Lister, contributed significantly to developing protocols that minimize infection risks.
Recommended video:
Map of Lesson on Bacteriophage Infections
Microbiology
Microbiology is the branch of science that studies microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. It encompasses various sub-disciplines, such as bacteriology, virology, and mycology, and is essential for understanding the roles these organisms play in health, disease, and the environment. Pioneers like Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch laid the groundwork for microbiological research and its applications in medicine.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Microbiology
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of how diseases spread and can be controlled within populations. It involves analyzing patterns, causes, and effects of health and disease conditions, which is crucial for developing effective infection control strategies. The work of scientists like John Snow, who investigated cholera outbreaks, has been foundational in linking epidemiology to public health and infection prevention.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: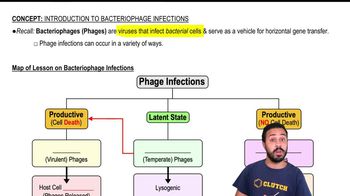


 1:29m
1:29m