Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycocalyces
Glycocalyces are sticky, gelatinous structures composed of polysaccharides and/or polypeptides that surround the cell wall of some bacteria. They play a crucial role in protecting bacteria from desiccation and immune responses, while also facilitating adherence to surfaces. In biofilm formation, glycocalyces help anchor bacterial cells together and to surfaces, creating a stable environment for microbial communities.
Recommended video:
The Glycocalyx: Capsules & Slime Layers
Fimbriae
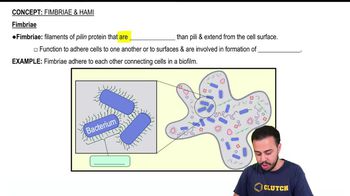
Fimbriae are short, hair-like appendages found on the surface of many bacteria, primarily composed of protein. They enable bacteria to adhere to surfaces and to each other, which is essential for the initial stages of biofilm formation. By facilitating close contact between cells, fimbriae enhance the structural integrity of biofilms and promote the exchange of genetic material among bacteria.
Recommended video:
Biofilm Formation
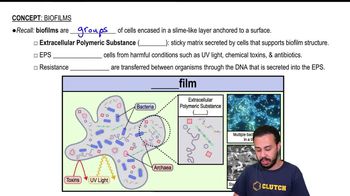
Biofilm formation is a process where microorganisms adhere to surfaces and each other, creating a structured community encased in a self-produced extracellular matrix. This matrix, often rich in polysaccharides, provides protection against environmental stresses and antibiotics. The combination of glycocalyces and fimbriae is vital in the initial attachment and subsequent development of biofilms, allowing for enhanced survival and resilience of microbial populations.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution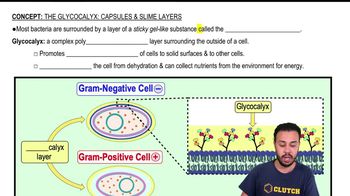

 3:14m
3:14m