Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is a cellular process in which certain cells, known as phagocytes, engulf and digest large particles, such as pathogens or dead cells. This process is crucial for the immune response, allowing the body to eliminate harmful microorganisms and debris. Phagocytes recognize these particles through receptors that bind to specific molecules on their surface.
Recommended video:
Steps of Phagocytosis
The steps of phagocytosis typically include: 1) recognition and attachment of the particle to the phagocyte, 2) engulfment of the particle into a phagosome, 3) fusion of the phagosome with lysosomes to form a phagolysosome, 4) digestion of the particle by enzymes, and 5) expulsion of indigestible material. Each step is essential for the effective clearance of pathogens.
Recommended video:
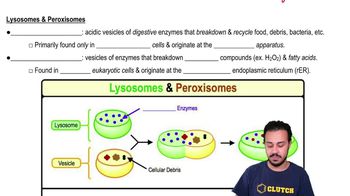
Role of Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes that play a critical role in phagocytosis. After a phagocyte engulfs a pathogen, the phagosome merges with lysosomes, forming a phagolysosome where the pathogen is broken down. This enzymatic digestion is vital for the destruction of harmful microorganisms and the recycling of cellular components.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution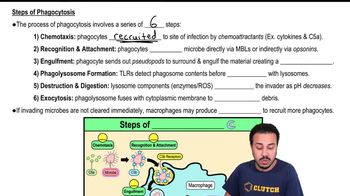


 2:19m
2:19m