Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) Technology
Recombinant DNA technology involves combining DNA from different sources to create new genetic combinations. This process often includes the use of enzymes to cut and join DNA fragments, allowing scientists to manipulate genes for various applications, such as gene cloning or the production of proteins. Understanding rDNA is crucial for designing experiments that involve gene expression and manipulation.
Recommended video:
Map of DNA-Based Technology Lesson
Transcription and Reverse Transcription
Transcription is the process by which RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA from a DNA template, transcribing the exons (coding regions) while excluding introns (non-coding regions). In contrast, reverse transcription is the process where reverse transcriptase converts mRNA back into cDNA (complementary DNA). This cDNA can then be used in various applications, including cloning and gene expression analysis.
Recommended video:
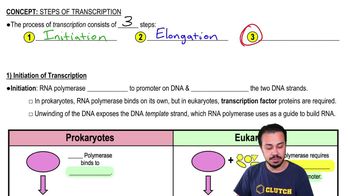
Initiation of Transcription
mRNA and cDNA
mRNA (messenger RNA) is the product of transcription and carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis. cDNA (complementary DNA) is synthesized from mRNA using reverse transcriptase and serves as a stable form of the gene that can be cloned or analyzed. Understanding the relationship between mRNA and cDNA is essential for experiments involving gene expression and the study of specific genes.
Recommended video:
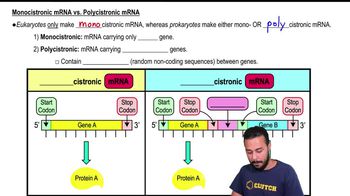
Monocistronic mRNA vs. Polycistronic mRNA
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 2:32m
2:32m