Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information within a biological system. It outlines the process by which DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into proteins. This framework is fundamental for understanding how genes dictate cellular functions and the synthesis of proteins, which are crucial for various biological processes.
Recommended video:
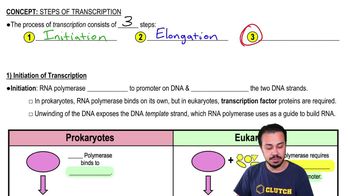
Transcription
Transcription is the first step in the central dogma, where the DNA sequence of a gene is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA). This process occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and involves the enzyme RNA polymerase, which binds to the DNA and synthesizes the mRNA strand. The resulting mRNA carries the genetic information needed for protein synthesis to the ribosomes.
Recommended video:
Initiation of Transcription
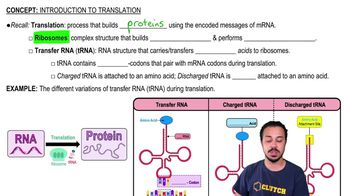
Translation
Translation is the second step in the central dogma, where the mRNA sequence is decoded to synthesize a specific protein. This process takes place in the ribosomes, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids that correspond to the codons on the mRNA. The sequence of amino acids determines the structure and function of the resulting protein, making translation a critical step in gene expression.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Translation
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution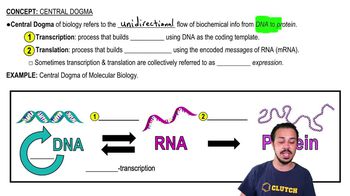

 5:45m
5:45m