Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Osmotic Lysis
Osmotic lysis occurs when a cell takes in water due to a difference in solute concentration across its membrane, leading to swelling and eventual rupture. This process is particularly relevant in cells without a rigid cell wall, as the internal pressure can exceed the membrane's capacity to contain it, resulting in cell death.
Recommended video:
2) Cell Lysis of Invading Microbes
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process where a cell loses water in a hypertonic environment, causing the cell membrane to pull away from the cell wall. This can lead to cell shrinkage and dysfunction, but it is distinct from lysis, as it does not involve rupture of the cell membrane.
Recommended video:
Mitochondria & Chloroplasts Example 1
Cell Membrane Integrity
The integrity of the cell membrane is crucial for maintaining homeostasis within the cell. Damage to the membrane can lead to leakage of essential cellular components, loss of ion gradients, and ultimately cell death, as the membrane serves as a barrier to protect the internal environment from external changes.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution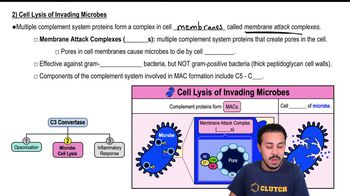



 2:10m
2:10m