Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Biofilms
Biofilms are structured communities of microorganisms that adhere to surfaces and are embedded in a self-produced extracellular matrix. They can form on various surfaces, including natural environments like rocks and artificial structures, and are not limited to aquatic settings. Biofilms play crucial roles in nutrient cycling, environmental stability, and can impact human health and industry.
Recommended video:
Aquatic Environments
Aquatic environments refer to water-based ecosystems, including freshwater and marine systems. These environments provide unique conditions for microbial life, such as nutrient availability and moisture, which facilitate the formation of biofilms. However, biofilms can also develop in terrestrial environments, indicating that their formation is not restricted to aquatic settings.
Recommended video:
Microbial Ecology
Microbial ecology is the study of the interactions between microorganisms and their environments, including their relationships with each other and with larger organisms. Understanding microbial ecology is essential for comprehending how biofilms form, their ecological roles, and their implications for health and industry. This field highlights the diversity of microbial life and the importance of environmental factors in shaping microbial communities.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Microbial Genetics
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution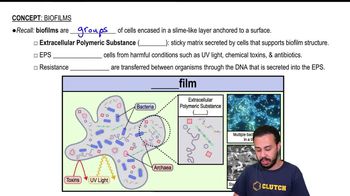



 3:31m
3:31m