Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs)
Toll-like receptors are a class of proteins that play a crucial role in the immune system by recognizing pathogens. They are located on the surface of immune cells and detect specific components of microbes, such as proteins and polysaccharides. This recognition triggers an immune response, helping the body to respond to infections.
Recommended video:
Innate Immunity
Innate immunity is the body's first line of defense against pathogens, providing immediate but non-specific responses. It includes physical barriers like skin, as well as immune cells that respond quickly to infections. TLRs are integral to this system, as they help identify and initiate responses to invading microbes.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Innate Immunity
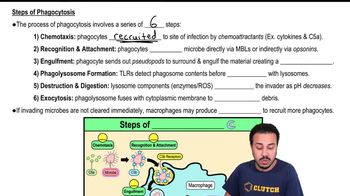
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is a process by which certain immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, engulf and digest pathogens. This mechanism is essential for clearing infections and involves the recognition of microbes, often facilitated by receptors like TLRs. Once a pathogen is engulfed, it is enclosed in a vesicle and destroyed by enzymes.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution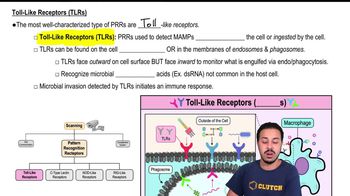


 2:59m
2:59m