Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells that contain digestive enzymes. They play a crucial role in breaking down waste materials and cellular debris. By fusing with phagosomes, which are formed during the process of phagocytosis, lysosomes help in the degradation of engulfed pathogens or particles.
Recommended video:
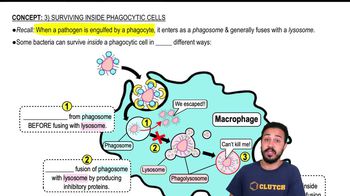
Phagosomes
Phagosomes are vesicles formed around a particle that has been engulfed by a cell through phagocytosis. They contain the ingested material and eventually fuse with lysosomes to form phagolysosomes, where the material is digested. Understanding the role of phagosomes is essential for comprehending how cells eliminate pathogens and maintain homeostasis.
Recommended video:
Surviving Inside Phagocytic Cells
Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes are organelles that contain enzymes for oxidative reactions, including the breakdown of fatty acids and the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide. Unlike lysosomes, peroxisomes do not primarily function in the degradation of engulfed materials. Recognizing the distinct functions of these organelles is vital for accurately interpreting cellular processes.
Recommended video:
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution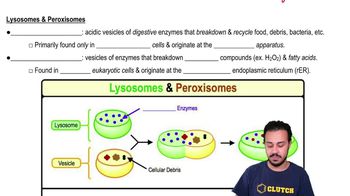


 2:19m
2:19m