Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Microbiology3h 27m
- Introduction to Microbiology18m
- Introduction to Taxonomy26m
- Scientific Naming of Organisms9m
- Members of the Bacterial World10m
- Introduction to Bacteria9m
- Introduction to Archaea10m
- Introduction to Eukarya20m
- Acellular Infectious Agents: Viruses, Viroids & Prions19m
- Importance of Microorganisms25m
- Scientific Method27m
- Experimental Design30m
- 2. Disproving Spontaneous Generation1h 18m
- 3. Chemical Principles of Microbiology3h 36m
- 4. Water1h 28m
- 5. Molecules of Microbiology2h 28m
- 6. Cell Membrane & Transport3h 28m
- Cell Envelope & Biological Membranes12m
- Bacterial & Eukaryotic Cell Membranes8m
- Archaeal Cell Membranes18m
- Types of Membrane Proteins8m
- Concentration Gradients and Diffusion9m
- Introduction to Membrane Transport14m
- Passive vs. Active Transport13m
- Osmosis33m
- Simple and Facilitated Diffusion17m
- Active Transport30m
- ABC Transporters11m
- Group Translocation7m
- Types of Small Molecule Transport Review9m
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis15m
- 7. Prokaryotic Cell Structures & Functions5h 52m
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells26m
- Binary Fission11m
- Generation Times16m
- Bacterial Cell Morphology & Arrangements35m
- Overview of Prokaryotic Cell Structure10m
- Introduction to Bacterial Cell Walls26m
- Gram-Positive Cell Walls11m
- Gram-Negative Cell Walls20m
- Gram-Positive vs. Gram-Negative Cell Walls11m
- The Glycocalyx: Capsules & Slime Layers12m
- Introduction to Biofilms6m
- Pili18m
- Fimbriae & Hami7m
- Introduction to Prokaryotic Flagella12m
- Prokaryotic Flagellar Structure18m
- Prokaryotic Flagellar Movement11m
- Proton Motive Force Drives Flagellar Motility5m
- Chemotaxis14m
- Review of Prokaryotic Surface Structures8m
- Prokaryotic Ribosomes16m
- Introduction to Bacterial Plasmids13m
- Cell Inclusions9m
- Endospores16m
- Sporulation5m
- Germination5m
- 8. Eukaryotic Cell Structures & Functions2h 18m
- 9. Microscopes2h 46m
- Introduction to Microscopes8m
- Magnification, Resolution, & Contrast10m
- Introduction to Light Microscopy5m
- Light Microscopy: Bright-Field Microscopes23m
- Light Microscopes that Increase Contrast16m
- Light Microscopes that Detect Fluorescence16m
- Electron Microscopes14m
- Reviewing the Different Types of Microscopes10m
- Introduction to Staining5m
- Simple Staining14m
- Differential Staining6m
- Other Types of Staining11m
- Reviewing the Types of Staining8m
- Gram Stain13m
- 10. Dynamics of Microbial Growth4h 37m
- Biofilms16m
- Growing a Pure Culture5m
- Microbial Growth Curves in a Closed System21m
- Temperature Requirements for Microbial Growth18m
- Oxygen Requirements for Microbial Growth22m
- pH Requirements for Microbial Growth8m
- Osmolarity Factors for Microbial Growth14m
- Reviewing the Environmental Factors of Microbial Growth12m
- Nutritional Factors of Microbial Growth31m
- Growth Factors4m
- Introduction to Cultivating Microbial Growth5m
- Types of Solid Culture Media4m
- Plating Methods16m
- Measuring Growth by Direct Cell Counts9m
- Measuring Growth by Plate Counts14m
- Measuring Growth by Membrane Filtration6m
- Measuring Growth by Biomass15m
- Introduction to the Types of Culture Media5m
- Chemically Defined Media3m
- Complex Media4m
- Selective Media5m
- Differential Media9m
- Reducing Media4m
- Enrichment Media7m
- Reviewing the Types of Culture Media8m
- 11. Controlling Microbial Growth4h 10m
- Introduction to Controlling Microbial Growth29m
- Selecting a Method to Control Microbial Growth44m
- Physical Methods to Control Microbial Growth49m
- Review of Physical Methods to Control Microbial Growth7m
- Chemical Methods to Control Microbial Growth16m
- Chemicals Used to Control Microbial Growth6m
- Liquid Chemicals: Alcohols, Aldehydes, & Biguanides15m
- Liquid Chemicals: Halogens12m
- Liquid Chemicals: Surface-Active Agents17m
- Other Types of Liquid Chemicals14m
- Chemical Gases: Ethylene Oxide, Ozone, & Formaldehyde13m
- Review of Chemicals Used to Control Microbial Growth11m
- Chemical Preservation of Perishable Products10m
- 12. Microbial Metabolism5h 21m
- Introduction to Energy15m
- Laws of Thermodynamics15m
- Chemical Reactions9m
- ATP22m
- Enzymes14m
- Enzyme Activation Energy9m
- Enzyme Binding Factors9m
- Enzyme Inhibition10m
- Introduction to Metabolism8m
- Negative & Positive Feedback7m
- Redox Reactions22m
- Introduction to Aerobic Cellular Respiration25m
- Types of Phosphorylation14m
- Glycolysis19m
- Entner-Doudoroff Pathway11m
- Pentose-Phosphate Pathway10m
- Pyruvate Oxidation8m
- Krebs Cycle16m
- Electron Transport Chain19m
- Chemiosmosis7m
- Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration19m
- Fermentation & Anaerobic Respiration23m
- 13. Photosynthesis2h 31m
- 14. DNA Replication2h 28m
- 15. Central Dogma & Gene Regulation7h 18m
- Central Dogma7m
- Introduction to Transcription20m
- Steps of Transcription22m
- Transcription Termination in Prokaryotes7m
- Eukaryotic RNA Processing and Splicing20m
- Introduction to Types of RNA9m
- Genetic Code25m
- Introduction to Translation30m
- Steps of Translation23m
- Review of Transcription vs. Translation12m
- Prokaryotic Gene Expression25m
- Review of Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Gene Expression13m
- Introduction to Regulation of Gene Expression13m
- Prokaryotic Gene Regulation via Operons27m
- The Lac Operon21m
- Glucose's Impact on Lac Operon25m
- The Trp Operon20m
- Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon11m
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation9m
- Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications16m
- Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control22m
- Eukaryotic Post-Transcriptional Regulation28m
- Post-Translational Modification6m
- Eukaryotic Post-Translational Regulation13m
- 16. Microbial Genetics4h 44m
- Introduction to Microbial Genetics11m
- Introduction to Mutations20m
- Methods of Inducing Mutations15m
- Prototrophs vs. Auxotrophs13m
- Mutant Detection25m
- The Ames Test14m
- Introduction to DNA Repair5m
- DNA Repair Mechanisms37m
- Horizontal Gene Transfer18m
- Bacterial Transformation11m
- Transduction32m
- Introduction to Conjugation6m
- Conjugation: F Plasmids18m
- Conjugation: Hfr & F' Cells19m
- Genome Variability21m
- CRISPR CAS11m
- 17. Biotechnology3h 0m
- 18. Viruses, Viroids, & Prions4h 56m
- Introduction to Viruses20m
- Introduction to Bacteriophage Infections14m
- Bacteriophage: Lytic Phage Infections12m
- Bacteriophage: Lysogenic Phage Infections17m
- Bacteriophage: Filamentous Phage Infections8m
- Plaque Assays9m
- Introduction to Animal Virus Infections10m
- Animal Viruses: 1. Attachment to the Host Cell7m
- Animal Viruses: 2. Entry & Uncoating in the Host Cell19m
- Animal Viruses: 3. Synthesis & Replication22m
- Animal Viruses: DNA Virus Synthesis & Replication14m
- Animal Viruses: RNA Virus Synthesis & Replication22m
- Animal Viruses: Antigenic Drift vs. Antigenic Shift9m
- Animal Viruses: Reverse-Transcribing Virus Synthesis & Replication9m
- Animal Viruses: 4. Assembly Inside Host Cell8m
- Animal Viruses: 5. Release from Host Cell15m
- Acute vs. Persistent Viral Infections25m
- COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2)14m
- Plant Viruses12m
- Viroids6m
- Prions13m
- 19. Innate Immunity7h 15m
- Introduction to Immunity8m
- Introduction to Innate Immunity17m
- Introduction to First-Line Defenses5m
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Skin13m
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Mucous Membrane9m
- First-Line Defenses: Chemical Barriers24m
- First-Line Defenses: Normal Microflora5m
- Introduction to Cells of the Immune System15m
- Cells of the Immune System: Granulocytes29m
- Cells of the Immune System: Agranulocytes25m
- Introduction to Cell Communication5m
- Cell Communication: Surface Receptors & Adhesion Molecules16m
- Cell Communication: Cytokines27m
- Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)45m
- Introduction to the Complement System24m
- Activation Pathways of the Complement System23m
- Effects of the Complement System23m
- Review of the Complement System12m
- Phagoctytosis21m
- Introduction to Inflammation18m
- Steps of the Inflammatory Response26m
- Fever8m
- Interferon Response25m
- 20. Adaptive Immunity7h 14m
- Introduction to Adaptive Immunity32m
- Antigens12m
- Introduction to T Lymphocytes38m
- Major Histocompatibility Complex Molecules20m
- Activation of T Lymphocytes21m
- Functions of T Lymphocytes25m
- Review of Cytotoxic vs Helper T Cells13m
- Introduction to B Lymphocytes27m
- Antibodies14m
- Classes of Antibodies35m
- Outcomes of Antibody Binding to Antigen15m
- T Dependent & T Independent Antigens21m
- Clonal Selection20m
- Antibody Class Switching17m
- Affinity Maturation14m
- Primary and Secondary Response of Adaptive Immunity21m
- Immune Tolerance28m
- Regulatory T Cells10m
- Natural Killer Cells16m
- Review of Adaptive Immunity25m
- 21. Principles of Disease6h 57m
- Symbiotic Relationships12m
- The Human Microbiome46m
- Characteristics of Infectious Disease47m
- Stages of Infectious Disease Progression26m
- Koch's Postulates26m
- Molecular Koch's Postulates11m
- Bacterial Pathogenesis36m
- Introduction to Pathogenic Toxins6m
- Exotoxins Cause Damage to the Host40m
- Endotoxin Causes Damage to the Host13m
- Exotoxins vs. Endotoxin Review13m
- Immune Response Damage to the Host15m
- Introduction to Avoiding Host Defense Mechanisms8m
- 1) Hide Within Host Cells5m
- 2) Avoiding Phagocytosis31m
- 3) Surviving Inside Phagocytic Cells10m
- 4) Avoiding Complement System9m
- 5) Avoiding Antibodies25m
- Viruses Evade the Immune Response27m
- 25. Epidemiology2h 24m
- Introduction to Epidemiology37m
- Introduction to Chain of Infection5m
- Reservoirs of Infection12m
- Disease Transmission4m
- Horizontal Disease Transmission30m
- Colonization of Susceptible Host7m
- Factors Influencing Epidemiology11m
- Emerging Infectious Diseases12m
- Healthcare-Associated Infections13m
- Epidemiological Studies8m
- 26. Applications of the Immune Response2h 9m
- 27. Immunological Disorders3h 29m
- 28. Antimicrobial Drugs3h 38m
- Introduction to Antimicrobial Drugs8m
- How Antimicrobial Drugs Work10m
- Broad vs Narrow Spectrum Drugs9m
- Superinfections11m
- Drug Interactions: Synergism and Antagonism8m
- Therapeutic Window & Therapeutic Index6m
- Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis: Beta-lactam & Penicillin36m
- Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis: Polypeptide Antibiotics & Isoniazid8m
- Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis11m
- Disruptors of Cell Membranes11m
- Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis9m
- Competitive Inhibitors of Metabolic Pathways12m
- Antifungal Drugs11m
- Antiviral Drugs10m
- Tests to Guide Antimicrobial Use21m
- Antimicrobial Resistance29m
- 29. Microbial Infections - Skin and Eyes46m
- 30. Microbial Infections - Respiratory System1h 23m
- 31. Microbial Infections - Digestive System1h 10m
- 34. Microbial Infections - Urogenital System1h 40m
10. Dynamics of Microbial Growth
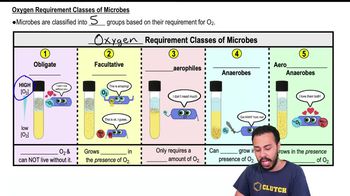
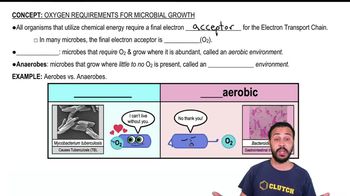
Oxygen Requirements for Microbial Growth

Reactive Oxygen Species
Jason Amores Sumpter
Video duration:
4mPlay a video: