Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR is a widely used technique in molecular biology that allows for the amplification of specific DNA sequences. By using cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension, PCR can produce millions of copies of a target DNA segment from a small initial sample. This method is essential for various applications, including cloning, gene expression analysis, and genetic testing.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction
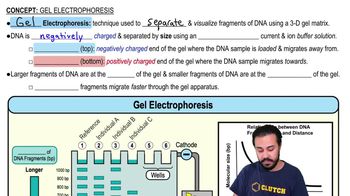
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory method used to separate DNA, RNA, or proteins based on their size and charge. In this technique, samples are placed in a gel matrix and subjected to an electric field, causing the molecules to migrate. While it is crucial for analyzing DNA fragments, it does not replicate DNA but rather visualizes the results of amplification or other processes.
Recommended video:
Electroporation
Electroporation is a technique used to introduce DNA into cells by applying an electrical field, which temporarily permeabilizes the cell membrane. This allows for the uptake of plasmids or other DNA molecules, facilitating genetic transformation. Although it is important for gene delivery, it does not replicate DNA; instead, it aids in the introduction of DNA into host cells.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 1:31m
1:31m