Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
RNA Polymerase Function
RNA polymerase is an enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA from a DNA template during the process of transcription. Unlike DNA polymerase, which requires a primer to initiate synthesis, RNA polymerase can start RNA synthesis de novo, meaning it can begin the process without a pre-existing strand. This allows for the rapid production of RNA molecules, which are essential for protein synthesis and gene regulation.
Recommended video:
DNA Polymerase Function
DNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides complementary to a template strand during DNA replication. It requires a primer to initiate synthesis and is involved in proofreading and correcting errors in the newly synthesized DNA. This ensures the fidelity of genetic information is maintained during cell division, which is crucial for genetic stability.
Recommended video:
Transcription vs. Replication
Transcription and replication are two fundamental processes in molecular biology. Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA, primarily involving RNA polymerase, while replication is the duplication of the entire DNA molecule, involving DNA polymerase. These processes differ in their purpose, with transcription focusing on gene expression and replication ensuring genetic continuity during cell division.
Recommended video:
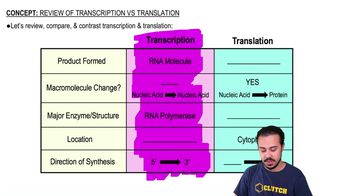
Review of Transcription vs. Translation
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 5:51m
5:51m