Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cytokines
Cytokines are small proteins that are crucial for cell signaling in the immune system. They are produced by various cells and play a key role in mediating and regulating immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. Examples include tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interferons, which help coordinate the body's response to infection and disease.
Recommended video:
Types of Cytokines
Cytokines can be classified into several categories based on their functions, including pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Chemokines, a subset of cytokines, are specifically involved in the chemotaxis of immune cells to sites of infection or injury. Understanding these categories helps in identifying which substances are considered cytokines.
Recommended video:
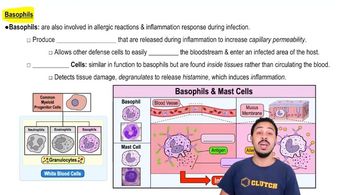
Eicosanoids and Histamine
Eicosanoids are signaling molecules derived from fatty acids and are involved in various physiological processes, including inflammation, but they are not classified as cytokines. Histamine, a biogenic amine, is primarily involved in allergic responses and gastric acid secretion, rather than immune signaling like cytokines. Recognizing the distinction between these molecules is essential for answering the question accurately.
Recommended video: