Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Endocytosis
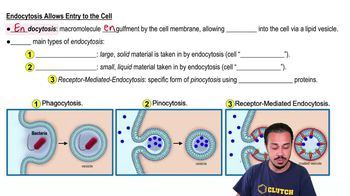
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell by engulfing them in a membrane-bound vesicle. This process is crucial for nutrient uptake, signaling, and maintaining cellular homeostasis. It includes various forms, such as phagocytosis and pinocytosis, which differ in the size and type of material being internalized.
Recommended video:
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis, often referred to as 'cell drinking,' is a specific type of endocytosis where the cell engulfs extracellular fluid along with dissolved solutes. This process allows cells to sample their environment and take in small molecules and nutrients. It is a non-specific mechanism, meaning it does not target specific substances.
Recommended video:
Endocytosis Allows Entry to the Cell
Vesicle Formation
Vesicle formation is a critical step in endocytosis, where the cell membrane invaginates to form a pocket that eventually pinches off to create a vesicle. This vesicle then transports the ingested material into the cell. The dynamics of vesicle formation are essential for understanding how cells regulate their internal environment and respond to external stimuli.
Recommended video:
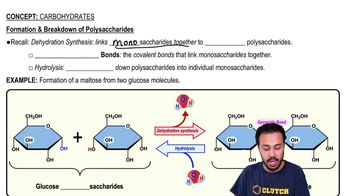
Formation & Breakdown of Polysaccharides
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution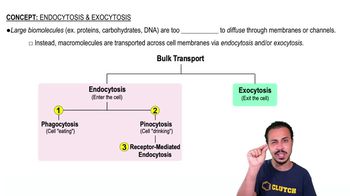

 2:02m
2:02m