Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Thylakoids
Thylakoids are membrane-bound structures found in chloroplasts of plants and in the cells of phototrophic bacteria. They contain chlorophyll and other pigments that capture light energy during photosynthesis. In phototrophic bacteria, thylakoids play a crucial role in converting light energy into chemical energy, which is essential for the organism's metabolic processes.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Photosystems
Phototrophic Bacteria
Phototrophic bacteria are a group of microorganisms that obtain energy from light through photosynthesis. They can be classified into two main types: oxygenic, which produce oxygen as a byproduct, and anoxygenic, which do not. These bacteria utilize pigments located in thylakoids to capture light energy, enabling them to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds.
Recommended video:
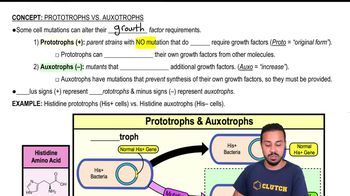
Prototrophs vs. Auxotrophs
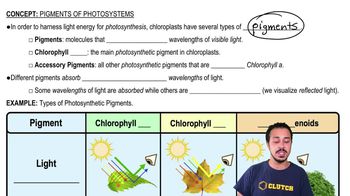
Pigments
Pigments are molecules that absorb specific wavelengths of light and are crucial for photosynthesis. In phototrophic bacteria, pigments such as bacteriochlorophyll are located in thylakoids and are responsible for trapping light energy. The absorbed light energy is then used to drive metabolic processes, including the synthesis of ATP and organic molecules.
Recommended video:
Pigments of Photosynthesis
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution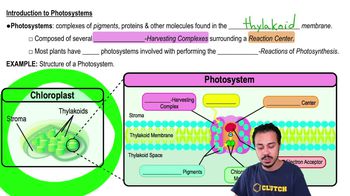

 2:42m
2:42m
