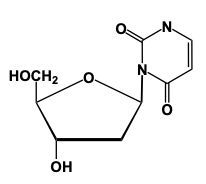
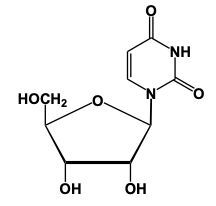
Now when it comes to nucleoside formation, we're going to say that our sugar and base form a glycosidic bond between the anomeric carbon, which is carbon number 1 of a sugar, and the nitrogen of our nitrogenous base. If we take a look here, we're going to say this sugar has an OH group on Carbon number 2. So this means that this represents a ribose sugar. Here, it's reacting with our nitrogenous base. Based on the memory tools that we learned from our previous topic, we know that this nitrogenous base would represent uracil. Now, here what's going to happen is we're going to have the anomeric carbon, this carbon here with its OH interacting with the hydrogen of this nitrogenous base. So, we're going to see that this represents a condensation reaction type reaction, where we're going to lose water. So just think of it like this, we have this OH, we have this H, we're going to lose water, that's gone away, but we need to basically replenish the bonds that we lost. Carbon lost the bond to an OH, nitrogen lost the bond to an H. So, they're going to bond to each other. Doing that helps us to create our glycosidic bond. And what do we have at the end? Well, we have a pentose sugar or pentose ring here, and we have our nitrogenous base. Remember, those two components help to make a nucleoside. And then here goes the water that we lost.
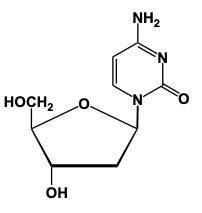
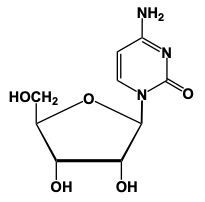
We come down here, what's the difference now? Well, here we no longer have an OH on carbon number 2, we've lost it. We still have an H there that's invisible, remember? Carbon still wants to make 4 bonds. Because we lost an oxygen, this represents a 2-deoxyribose sugar. And then, here, we're looking at this purine, and we know that this purine, based on the memory tools that we've learned earlier, this sugar here, well, this nitrogenous base here represents adenine. Again, think of it as a condensation reaction where we lose H, N, and OH in the form of water. And carbon and nitrogen now, bond to each other. So, we make our glycosidic bond right here. Again, we have our pentose ring with an nitrogenous base. So, again, we've made a nucleoside. So, just remember, this basically is what we deal with when it comes to nucleoside formation where we have the anomeric carbon interac... Environment remains undefined.