25. Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism
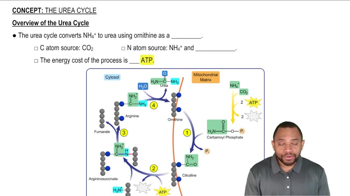
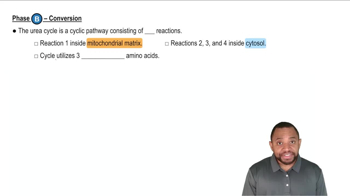
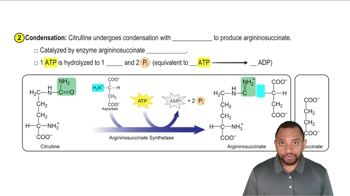
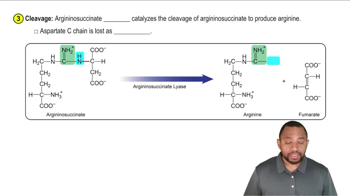
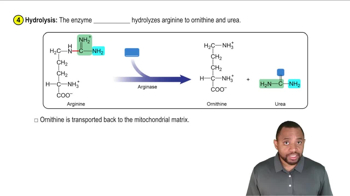
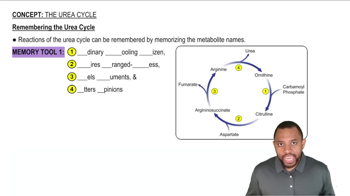
The Urea Cycle
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which amino acid provides the NH4+ for the formation of carbamoyl phosphate?
103views - Multiple Choice
Which of the following amino acids is not a part of the urea cycle?
30views - Multiple Choice
What is the function of aspartate in the urea cycle?
40views - Multiple Choice
Which one of the following sentences is an incorrect description of a reaction in the urea cycle?
26views - Textbook Question
Fumarate from step 3 of the urea cycle may be recycled into aspartate for use in step 2 of the cycle. The sequence of reactions for this process is
a. <IMAGE>
b. <IMAGE>
c. <IMAGE>
Classify each reaction as one of the following:
1. Oxidation
2. Reduction
3. Transamination
4. Elimination
5. Addition
37views - Textbook Question
In the liver, the relative activity of ornithine transcarbamylase is high, that of argininosuccinate synthetase is low, and that of arginase is high. Why is it important that ornithine transcarbamylase activity be high in the liver? What might be the consequence if arginase activity is low or defective?
32views - Textbook Question
From what two amino acids do the nitrogens in urea arise? (Hint: See Figure 25.3.)
20views - Textbook Question
The net reaction for the urea cycle shows that three ATPs are hydrolyzed; however, the total energy “cost” is four ATPs. Explain why this is true.
164views