- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

What is the implication when we say that the enzyme is fully occupied by a substrate? How does adding more enzyme and substrate influence the rate of the chemical reaction?
In a biochemistry lab, students conducted an experiment to compare the enzyme activity in spinach and lettuce leaves. They first observed the color change in both leaves when exposed to air due to phenolase activity. Then, they performed another experiment where they added hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to fresh spinach and lettuce samples and recorded the time until bubbles appeared. Which sample has more catalase? Explain your answer.
Papaya has papain that can hydrolyze peptide bonds in the proteins. In the process of marinating a tough meat, why is fresh papaya used?
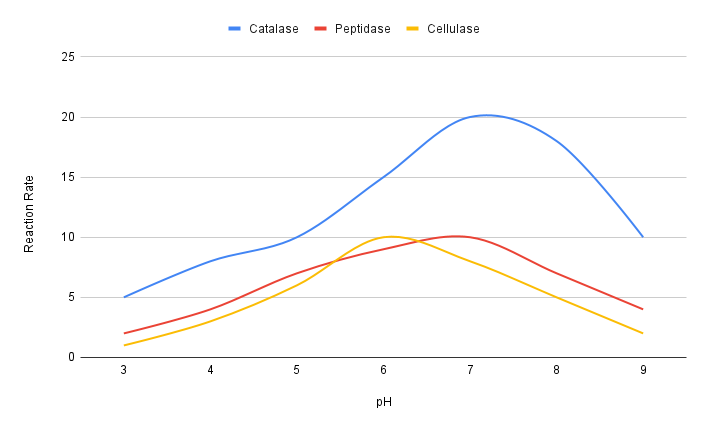
The graph below illustrates the relationship between enzyme activity and pH for catalase, peptidase, and cellulase. Based on the graph, which of the following optimal pH is correct?
If the temperature is raised from 37°C to 70°C, how would this change affect the activity of an enzyme that functions optimally at normal body temperature and physiological pH?
I. The enzyme’s activity will decrease as the temperature rises from 37°C to 70°C, improving the rate of reaction.
II. The enzyme’s activity will decrease because the high temperature will likely denature the enzyme, reducing its effectiveness.
III. The enzyme may become completely inactive at 70°C due to irreversible denaturation.
IV. The enzyme’s activity will initially increase as the temperature rises but then decrease sharply as it approaches 70°C due to denaturation.
Trypsin is an enzyme that hydrolyzes proteins by cutting off peptide bonds, functioning optimally in the small intestine at a pH of 7.5 to 8.5. How would increasing the concentration of proteins affect the rate of a reaction catalyzed by trypsin? (Select all that apply)
I. The reaction rate will increase as the concentration of proteins increases, up to a point where the enzyme becomes saturated.
II. The reaction rate will remain constant regardless of changes in protein concentration once all enzyme active sites are occupied.
III. The reaction rate will plateau as the enzyme becomes fully saturated and cannot process additional substrate molecules.
IV. The reaction rate will decrease as excess proteins might interfere with the enzyme's activity.
Proteins in meat are broken down by enzymes, leading to spoilage. Drying fresh meats effectively preserves them for extended periods. How does drying meat help prevent spoilage by affecting enzymatic activity?