Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
ß-keto acid
A ß-keto acid is a type of organic compound that contains a ketone group (C=O) adjacent to a carboxylic acid group (–COOH). This structure is significant in biochemistry as it plays a role in various metabolic pathways, including the citric acid cycle. The presence of both functional groups allows for unique reactivity, making ß-keto acids important intermediates in enzymatic reactions.
Recommended video:
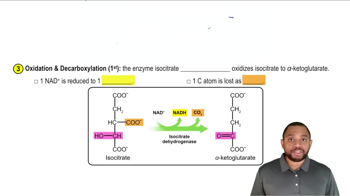
isocitrate dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate in the citric acid cycle. This enzyme is crucial for cellular respiration, as it helps convert energy stored in carbohydrates into usable forms. Understanding its mechanism and the intermediates it produces is essential for grasping metabolic processes.
Recommended video:
Phase B - Succinyl CoA Formation Concept 5
unstable intermediates
Unstable intermediates are transient species that form during chemical reactions and have a short lifespan before converting into more stable products. In enzymatic reactions, these intermediates can influence the reaction rate and pathway. Recognizing these intermediates is vital for understanding the dynamics of metabolic pathways and the role of enzymes in facilitating these transformations.
Recommended video:
Overview of Protein Synthesis Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 :55m
:55m