Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
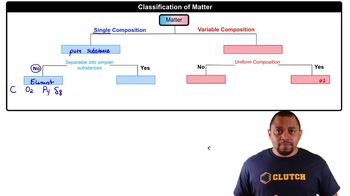
Homogeneous Mixtures
Homogeneous mixtures are uniform in composition and appearance, meaning that the individual components are not distinguishable. An example is a solution where the solute is completely dissolved in the solvent, such as saltwater. In these mixtures, any sample taken will have the same composition throughout.
Recommended video:
Solubility and Intermolecular Forces Concept 1
Heterogeneous Mixtures
Heterogeneous mixtures consist of visibly different substances or phases. The components can often be separated by physical means, and their proportions can vary throughout the mixture. Examples include salad or a mixture of sand and gravel, where the individual components remain distinct.
Recommended video:
Solubility and Intermolecular Forces Concept 1
Classification of Mixtures
The classification of mixtures into homogeneous and heterogeneous is essential in chemistry and food science. This classification helps in understanding the properties and behaviors of different mixtures. For instance, tea, when brewed, is typically considered a homogeneous mixture because the tea leaves are not visible, and the flavor is evenly distributed throughout the liquid.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:34m
1:34m