Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkyl Halides
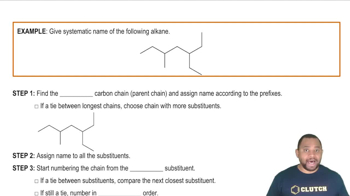
Alkyl halides are organic compounds derived from alkanes by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine). They are classified into primary, secondary, and tertiary based on the carbon atom to which the halogen is attached. Understanding the structure of alkyl halides is crucial for naming them systematically.
Recommended video:
IUPAC Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature provides a systematic method for naming chemical compounds. For alkyl halides, the name is derived from the longest carbon chain, followed by the halogen substituent, with appropriate numbering to indicate the position of the halogen. Familiarity with IUPAC rules is essential for accurately naming these compounds.
Recommended video:
Substituent Positioning
In the systematic naming of alkyl halides, the position of the halogen substituent on the carbon chain is indicated by a number. This number corresponds to the carbon atom to which the halogen is attached, ensuring clarity in the compound's structure. Correctly identifying and numbering the substituents is vital for providing an unambiguous name.
Recommended video:
Naming Alkanes with Substituents Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 :49m
:49m