Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is determined by the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom, which influences the shape of the molecule. Understanding molecular geometry is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of substances.
Recommended video:
Molecular Geometry (Simplified) Concept 1
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom. According to VSEPR, electron pairs will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion, leading to specific molecular shapes such as linear, trigonal planar, or tetrahedral.
Recommended video:
Hybridization
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals that can accommodate bonding in a molecule. In the case of methylamine (CH₃NH₂), the nitrogen atom undergoes sp³ hybridization, resulting in four equivalent hybrid orbitals that allow for the formation of bonds with hydrogen and carbon, influencing the overall shape of the molecule.
Recommended video:
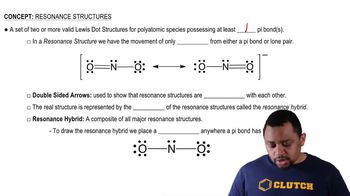
Resonance Structures (Simplified) Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution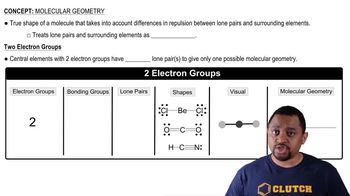


 1:10m
1:10m