Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Esterification Reaction
Esterification is a chemical reaction that forms an ester from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. In this process, the hydroxyl group (-OH) from the acid and a hydrogen atom from the alcohol combine to release water (H2O), resulting in the formation of the ester. This reaction is typically catalyzed by an acid, which helps to drive the reaction to completion.
Recommended video:
Ester Reactions: Esterification Example 1
Balanced Chemical Equation
A balanced chemical equation represents a chemical reaction with equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides of the equation. Balancing ensures the law of conservation of mass is upheld, meaning that matter is neither created nor destroyed in the reaction. This is crucial for accurately depicting the reactants and products involved in the formation of propyl acetate.
Recommended video:
Balancing Chemical Equations (Simplified) Concept 1
Chemical Structure of Propyl Acetate
Propyl acetate is an ester formed from propanol (an alcohol) and acetic acid (a carboxylic acid). Its chemical structure consists of a propyl group (C3H7) attached to an acetate group (C2H3O2). Understanding its structure is essential for writing the correct balanced equation, as it helps identify the reactants and products involved in the esterification process.
Recommended video:
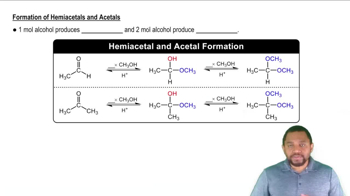
Formation of Hemiacetals and Acetals Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:5m
1:5m