Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solid
A solid is a state of matter characterized by a fixed shape and volume. The particles in a solid are closely packed together and vibrate in place, which gives solids their rigidity. Examples include ice, wood, and metals. Solids do not flow and maintain their shape unless subjected to sufficient force.
Recommended video:
Atomic, Ionic and Molecular Solids Concept 1
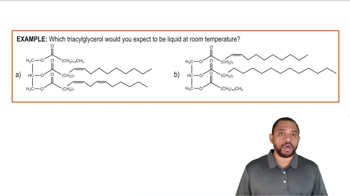
Liquid
A liquid is a state of matter that has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container. The particles in a liquid are less tightly packed than in a solid, allowing them to move freely and slide past one another. This property enables liquids to flow and conform to the shape of their surroundings, such as water or oil.
Recommended video:
Triacylglycerols Example 2
Gas
A gas is a state of matter that has neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume. The particles in a gas are far apart and move rapidly in all directions, which allows gases to expand and fill any available space. Common examples include oxygen, carbon dioxide, and helium. Gases are compressible and can change volume significantly under pressure.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution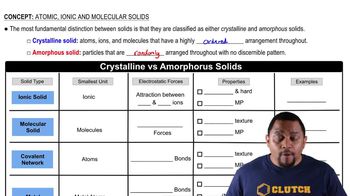


 1:35m
1:35m