Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dehydration Reaction
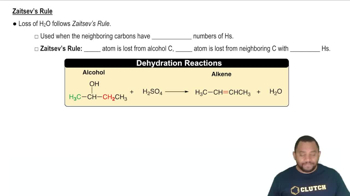
A dehydration reaction involves the removal of a water molecule from an alcohol, resulting in the formation of an alkene. This process typically requires an acid catalyst and can lead to the formation of multiple products, but the major product is determined by the stability of the resulting alkene, often following Zaitsev's rule.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
Zaitsev's Rule
Zaitsev's rule states that in elimination reactions, the more substituted alkene is usually the major product. This principle helps predict the outcome of dehydration reactions, as more stable alkenes (those with greater substitution) are favored due to lower energy and increased stability.
Recommended video:
Structure of Alkenes
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. The structure of an alkene, such as 1,4-pentadiene, is crucial for understanding its formation from alcohols. The positioning of the double bonds and the overall carbon skeleton influence the reactivity and properties of the alkene.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:3m
1:3m