Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH in the process. This occurs in the cytoplasm and is the first step in cellular respiration, providing the necessary substrates for the citric acid cycle. The ATP generated here is crucial for cellular functions, while NADH serves as an electron carrier for later stages.
Recommended video:
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, takes place in the mitochondria and processes acetyl-CoA derived from pyruvate. It generates additional NADH and FADH2, which are vital for the electron transport chain. This cycle is essential for the complete oxidation of glucose, contributing to the overall production of ATP through subsequent electron transport.
Recommended video:
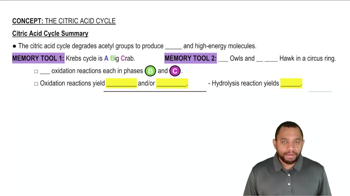
Citric Acid Cycle Summary Concept 12
Electron Transport Chain
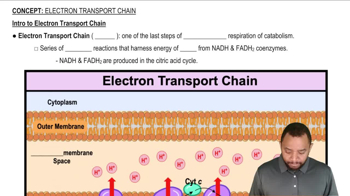
The electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen. This process creates a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis via ATP synthase. The ETC is the final stage of cellular respiration, where the majority of ATP is produced, linking the earlier stages of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to energy generation.
Recommended video:
Intro to Electron Transport Chain Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 2:46m
2:46m