Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. In the case of C₉H₂₀, isomers can vary in the connectivity of carbon atoms, leading to different physical and chemical properties despite having the same number of atoms.
Recommended video:
Straight-Chain Hydrocarbons
Straight-chain hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting of carbon atoms connected in a linear sequence, with hydrogen atoms filling the remaining valences. For C₉H₂₀, the straight-chain isomer would have all nine carbon atoms arranged in a single continuous line, which is the simplest structural form of this molecular formula.
Recommended video:
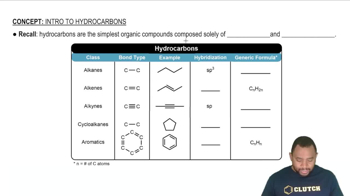
Intro to Hydrocarbons Concept 1
Structural Representation
Structural representation involves depicting the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, often using line-bond formulas or skeletal structures. For C₉H₂₀, drawing the straight-chain isomer requires accurately representing the nine carbon atoms and their associated hydrogen atoms, ensuring clarity in how the molecule is structured.
Recommended video:
Molecular Representations Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 2:8m
2:8m