Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
States of Matter
The states of matter refer to the distinct forms that different phases of matter take on. The primary states are solid, liquid, and gas, each characterized by unique properties such as shape, volume, and particle arrangement. Understanding these states is crucial for classifying substances like water (liquid) and iodine (solid) at room temperature.
Recommended video:
States of Matter Concept 1
Mixtures vs. Pure Substances
Mixtures consist of two or more substances that are physically combined, while pure substances have a uniform and definite composition. For example, air is a mixture of gases, whereas sodium bicarbonate is a pure chemical compound. Recognizing the difference helps in identifying substances like blood (a complex mixture) and gasoline (a mixture of hydrocarbons).
Recommended video:
Intensive vs. Extensive Properties
Chemical Elements and Compounds
Chemical elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances, while chemical compounds are formed when two or more elements chemically bond together. For instance, sodium bicarbonate is a compound made from sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen, whereas silicon is a chemical element. This distinction is essential for classifying substances like gaseous ammonia (a compound) and iodine (an element).
Recommended video:
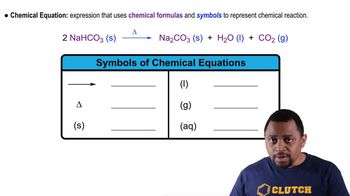
Chemical Reaction: Chemical Change Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:34m
1:34m