Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acids and Codons
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and each amino acid is encoded by a sequence of three nucleotides known as a codon. In the case of preproinsulin, which consists of 81 amino acids, the total number of codons required for its synthesis is 81, as each amino acid corresponds to one codon.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
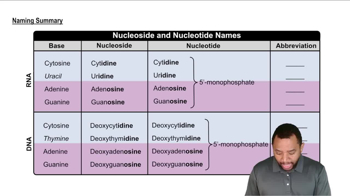
DNA and Nucleotides
DNA is composed of nucleotides, which include a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). Each codon in the DNA sequence is formed by a specific arrangement of these bases, and since each codon consists of three bases, the total number of bases needed can be calculated based on the number of codons.
Recommended video:
Naming Nucleosides and Nucleotides Concept 3
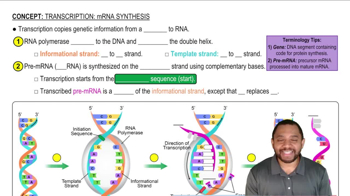
Transcription and Translation
Transcription is the process by which the DNA sequence is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA), which then undergoes translation to synthesize proteins. In this context, the informational DNA strand must be transcribed to produce mRNA that contains the codons for the 81 amino acids of preproinsulin, ensuring that the correct sequence of bases is present to code for the protein.
Recommended video:
Transcription: mRNA Synthesis Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 3:25m
3:25m