Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molar Mass Calculation
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). For calcium citrate, the molar mass is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all atoms in its formula, Ca(C6H5O7)2. This value is essential for converting between grams of the compound and moles, which is necessary for determining how much calcium citrate is needed to meet dietary requirements.
Recommended video:
Calcium Content in Calcium Citrate
Calcium citrate contains a specific percentage of elemental calcium by mass. To determine how much calcium citrate is required to meet the recommended daily intake of calcium, one must first know the calcium content in the compound. This involves calculating the mass of calcium in a given mass of calcium citrate, which is crucial for ensuring adequate calcium intake.
Recommended video:
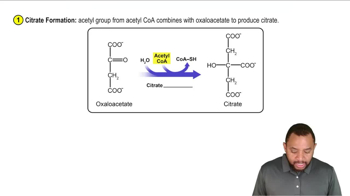
Phase A - Citrate Formation Concept 2
Recommended Daily Intake of Calcium
The recommended daily intake of calcium varies by age, sex, and life stage, typically ranging from 1,000 to 1,300 mg for adults. Understanding these guidelines is vital for determining how much calcium citrate is necessary to achieve the desired calcium intake. This ensures that individuals can maintain bone health and prevent deficiencies through proper supplementation.
Recommended video:
The Scientific Method Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution