Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Coenzymes
Coenzymes are organic molecules that assist enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions. They often act as carriers for chemical groups or electrons, facilitating the transfer of these components during metabolic processes. Understanding coenzymes is essential for grasping how enzymes function and the role of various molecules in cellular metabolism.
Recommended video:
NAD+ and NADH
NAD+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a coenzyme involved in redox reactions, playing a crucial role in energy metabolism. When it accepts electrons, it is reduced to form NADH, which carries energy and reducing power to various biochemical pathways. Recognizing the difference between NAD+ and its reduced form, NADH, is vital for understanding cellular respiration and energy production.
Recommended video:
Intro to Electron Transport Chain Example 1
Reduction and Oxidation
Reduction and oxidation (redox) are chemical processes that involve the transfer of electrons between substances. Reduction refers to the gain of electrons (or hydrogen) by a molecule, while oxidation is the loss of electrons (or hydrogen). This concept is fundamental in biochemistry, particularly in understanding how coenzymes like NAD+ and NADH function in metabolic pathways.
Recommended video:
Reduction of Monosaccharides Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution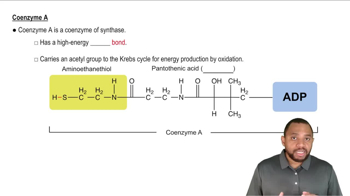



 2:2m
2:2m