Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Tollens' Reagent
Tollens' reagent is a solution of silver nitrate in ammonia, used to test for aldehydes. When an aldehyde is present, it reduces the silver ions to metallic silver, resulting in a characteristic silver mirror on the test container. This reagent does not react with ketones, making it a selective test for aldehydes.
Recommended video:
Benedict's Reagent
Benedict's reagent is a blue solution containing copper(II) sulfate, which is used to test for reducing sugars and aldehydes. When heated with a reducing sugar or an aldehyde, the copper(II) ions are reduced to copper(I) oxide, forming a colored precipitate ranging from green to brick red, depending on the amount of reducing sugar present.
Recommended video:
Aldehydes vs. Ketones
Aldehydes and ketones are both carbonyl compounds, but they differ in structure and reactivity. Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain, making them more reactive towards oxidizing agents like Tollens' and Benedict's reagents. In contrast, ketones have the carbonyl group within the carbon chain and generally do not react with these reagents, making their identification crucial in organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
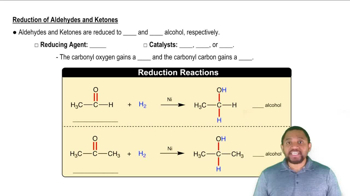
Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:57m
1:57m