Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acids and Side Chains
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid has a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group). The properties of the side chains determine the amino acid's characteristics, including its ability to participate in hydrogen bonding, which is crucial for protein structure and function.
Recommended video:
Intro to Amino Acids Concept 1
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is a type of weak chemical bond that occurs when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen, experiences an attraction to another electronegative atom. This interaction is significant in biological systems, as it stabilizes the structures of proteins and nucleic acids, and facilitates interactions with water molecules, influencing solubility and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Hydrogenation Reactions Concept 1
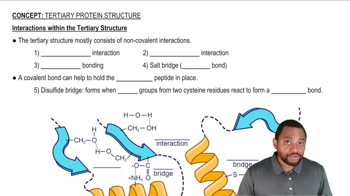
Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Interactions
Hydrophilic interactions refer to the affinity of molecules or side chains that can form hydrogen bonds with water, making them soluble in aqueous environments. In contrast, hydrophobic interactions involve nonpolar side chains that do not interact favorably with water. Understanding these interactions is essential for predicting how amino acids behave in proteins and how they interact with their environment, including water.
Recommended video:
Interactions within the Tertiary Structure Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution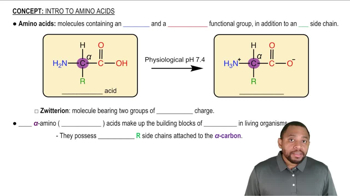


 5:16m
5:16m