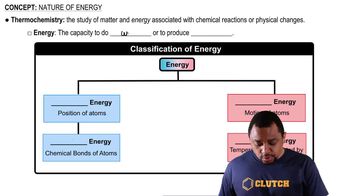
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Combustion of Glucose
The combustion of glucose is a chemical reaction where glucose reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. This process is exothermic and occurs rapidly, resulting in a significant release of energy that is not harnessed for biological work.
Recommended video:
Total Energy From Glucose Concept 1
Metabolic Oxidation
Metabolic oxidation of glucose occurs in living organisms through a series of enzymatic reactions, primarily in cellular respiration. This process is more controlled and occurs in stages, allowing the energy released to be captured in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which cells use for various biological functions.
Recommended video:
Glycerol Metabolism Example 1
Energy Transfer and Utilization
In combustion, energy is released as heat and light, which is often lost to the environment and cannot be used by organisms. In contrast, during metabolic oxidation, the energy is transferred to ATP, enabling cells to perform work, such as muscle contraction and biosynthesis, thus making it a more efficient and useful process for living systems.
Recommended video: