Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solubility
Solubility refers to the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a given volume of solvent at a specific temperature and pressure. In this case, the solubility of ammonia (NH₃) in water is provided at two different temperatures, indicating how temperature affects the amount of gas that can be dissolved in the liquid.
Recommended video:
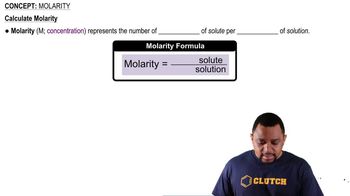
Molarity and Moles
Molarity is a measure of concentration, defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. To find the number of moles of NH₃ released when the temperature increases, one must calculate the difference in solubility at the two temperatures and then convert that difference into moles using the volume of the solution.
Recommended video:
Henry's Law
Henry's Law states that the amount of gas that dissolves in a liquid at a given temperature is proportional to the partial pressure of that gas above the liquid. This principle helps explain the changes in solubility of NH₃ with temperature, as increasing temperature typically decreases gas solubility, leading to the release of dissolved gas when the temperature rises.
Recommended video:
Henry's Law Calculations Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:41m
1:41m