Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cholesterol Structure and Function
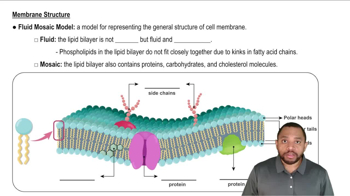
Cholesterol is a lipid molecule with a complex ring structure that plays a crucial role in cell membranes. It helps to maintain membrane fluidity by preventing the fatty acid chains of phospholipids from packing too closely together, which is essential for proper membrane function and flexibility.
Recommended video:
Membrane Fluidity
Membrane fluidity refers to the viscosity of the lipid bilayer of cell membranes, which affects how proteins and lipids move within the layer. Cholesterol contributes to this fluidity by acting as a buffer; it stabilizes the membrane at high temperatures and prevents it from becoming too rigid at low temperatures.
Recommended video:
Phospholipid Bilayer
The phospholipid bilayer is the fundamental structure of cell membranes, composed of two layers of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails facing inward. Cholesterol intersperses within this bilayer, influencing its properties and the overall integrity of the membrane.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 :50m
:50m