Textbook Question
What happens when a strong base such as KOH is dissolved in water?
2116
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

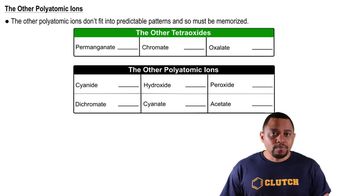
What happens when a strong base such as KOH is dissolved in water?
What happens when a weak base such as NH3 is dissolved in water?
What is the difference between a monoprotic acid and a diprotic acid? Give an example of each.
How is Kw defined, and what is its numerical value at 25 °C?
Rearrange the equation you wrote in Problem 10.50 to solve for [H3O+] in terms of Ka.
The pH of a buffer solution containing 0.10 M acetic acid and 0.10 M sodium acetate is 4.74.
a. Write the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation for this buffer.