Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions are chemical processes that release energy, usually in the form of heat, to the surroundings. This occurs when the total energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants, resulting in a net release of energy. A common example is the combustion of fuels, where energy is released as heat and light.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
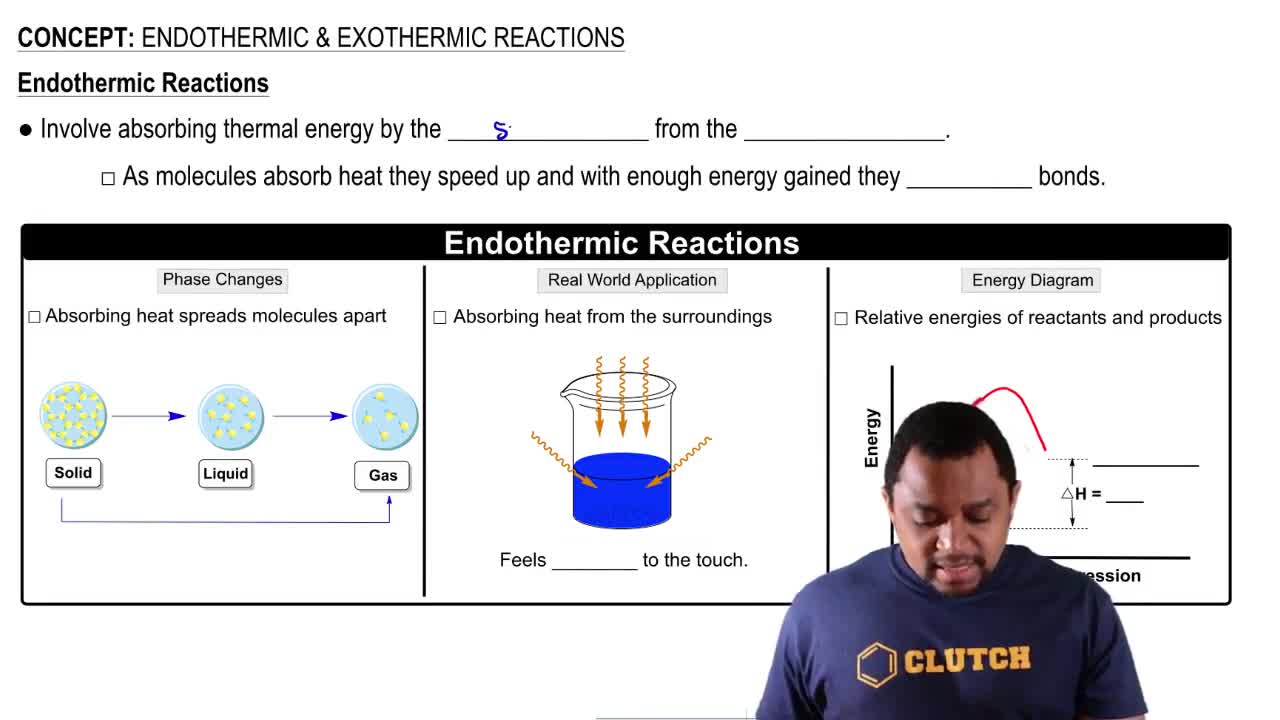
Endothermic Reactions
Endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings, leading to a decrease in temperature in the immediate environment. In these reactions, the energy of the products is higher than that of the reactants, requiring an input of energy to proceed. Photosynthesis is a classic example, where plants absorb sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Enthalpy Change (ΔH)
Enthalpy change, denoted as ΔH, is a measure of the heat content of a system during a chemical reaction. A negative ΔH indicates an exothermic reaction, where heat is released, while a positive ΔH signifies an endothermic reaction, where heat is absorbed. In the given reaction, the release of 802 kJ suggests that it is exothermic, as energy is being released to the surroundings.
Recommended video:
Physical & Chemical Changes
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution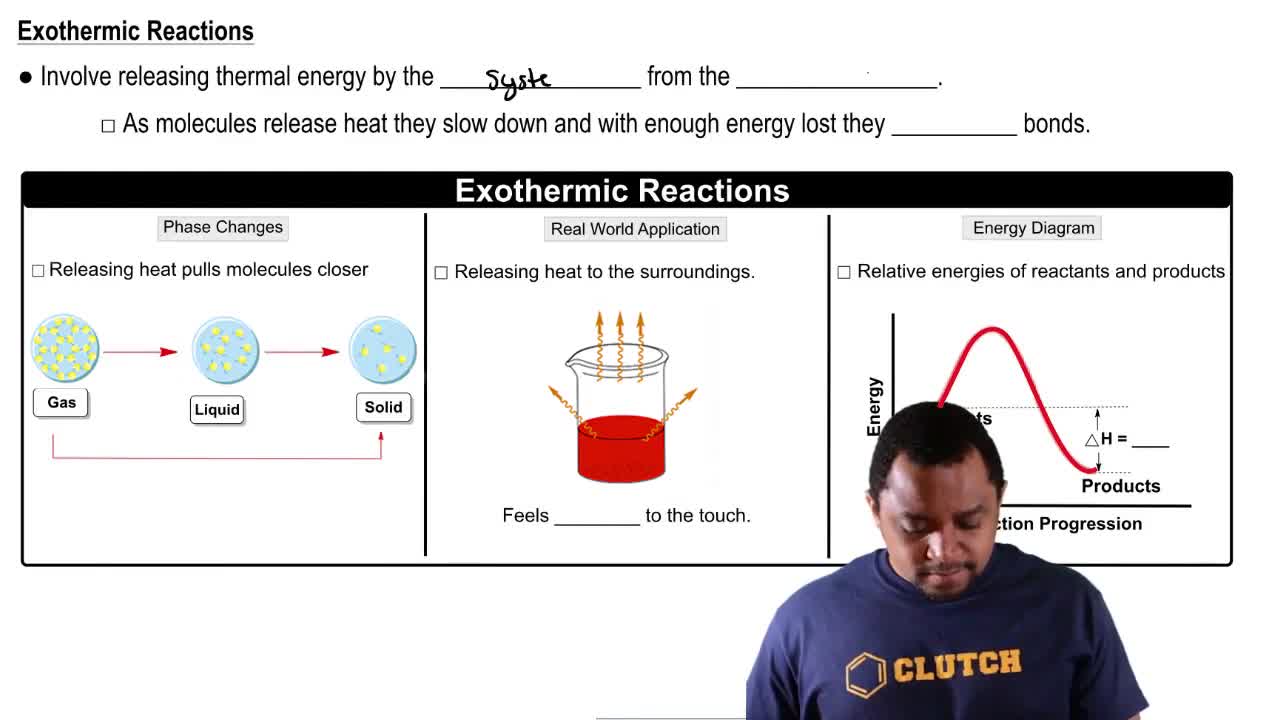


 2:30m
2:30m
