Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons consisting only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms, connected by single bonds. They follow the general formula CnH2n+2, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms. Alkanes are characterized by their relatively low reactivity and are commonly found in natural gas and petroleum.
Recommended video:
Tertiary Carbon
A tertiary carbon atom is a carbon atom that is bonded to three other carbon atoms. In the context of alkanes, this configuration affects the molecule's branching and stability. Tertiary carbons are significant in organic chemistry as they influence the reactivity and properties of the compound.
Recommended video:
Tertiary Protein Structure Concept 1
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms. In the case of a 5-carbon alkane with a tertiary carbon, there can be multiple structural isomers, each with unique properties and structures. Understanding isomerism is crucial for identifying and naming different alkanes.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution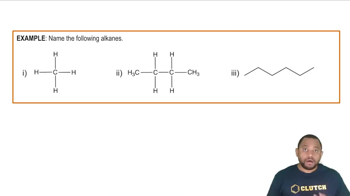



 2:26m
2:26m