Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ketosis
Ketosis is a metabolic state in which the body, due to a lack of carbohydrates, begins to break down fat for energy, producing ketones as a byproduct. This process typically occurs when carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, prompting the liver to convert fatty acids into ketones, which can be used as an alternative energy source by various tissues, including the brain.
Recommended video:
Low Carbohydrate Intake
A key condition for entering ketosis is a low carbohydrate intake, usually below 50 grams per day. This reduction in carbohydrates forces the body to deplete its glycogen stores and shift its primary energy source from glucose to fat. This dietary approach is often utilized in ketogenic diets to promote weight loss and improve metabolic health.
Recommended video:
Classification of Carbohydrates Example 1
Ketone Bodies
Ketone bodies are the three water-soluble molecules—acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone—produced during fat metabolism in the liver. These compounds serve as an alternative energy source when glucose is scarce, and their presence in the blood is a hallmark of ketosis. Monitoring ketone levels can help determine whether an individual has successfully entered this metabolic state.
Recommended video:
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution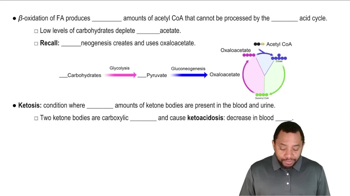



 1:29m
1:29m